Here is a review of reviews on the health effects of animal foods versus plant foods.
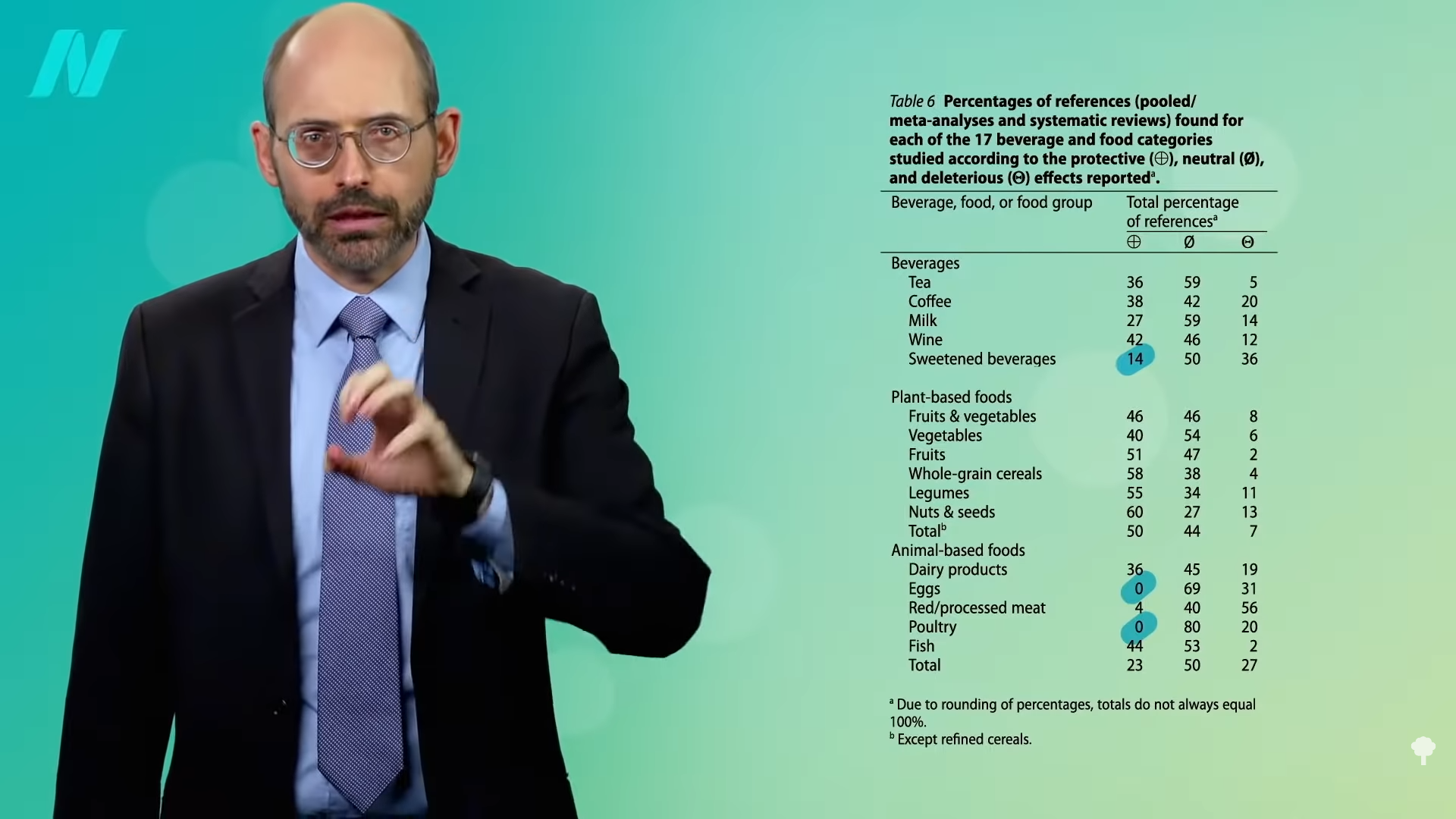
Instead of looking only at individual studies or individual reviews of studies, what if you looked at a review of reviews? In my last video, I covered beverages. As you can see below and at 0:20 in my video Friday Favorites: What Are the Best Foods?, the majority of reviews found some effects either way, finding at least some benefits to tea, coffee, wine, and milk, but not for sweetened beverages, such as soda. As I explored in depth, this approach isn’t perfect. It doesn’t take into account such issues as conflicts of interest and industry funding of studies, but it can offer an interesting bird’s-eye view of what’s out in the medical literature. So, what did the data show for food groups?

You’ll note the first thing the authors did was divide everything into plant-based foods or animal-based foods. For the broadest takeaway, we can look at the totals. The vast majority of reviews on whole plant foods show protective or, at the very least, neutral effects, whereas most reviews of animal-based foods identified deleterious health effects or, at best, neutral effects, as you can see at 1:14 in my video.
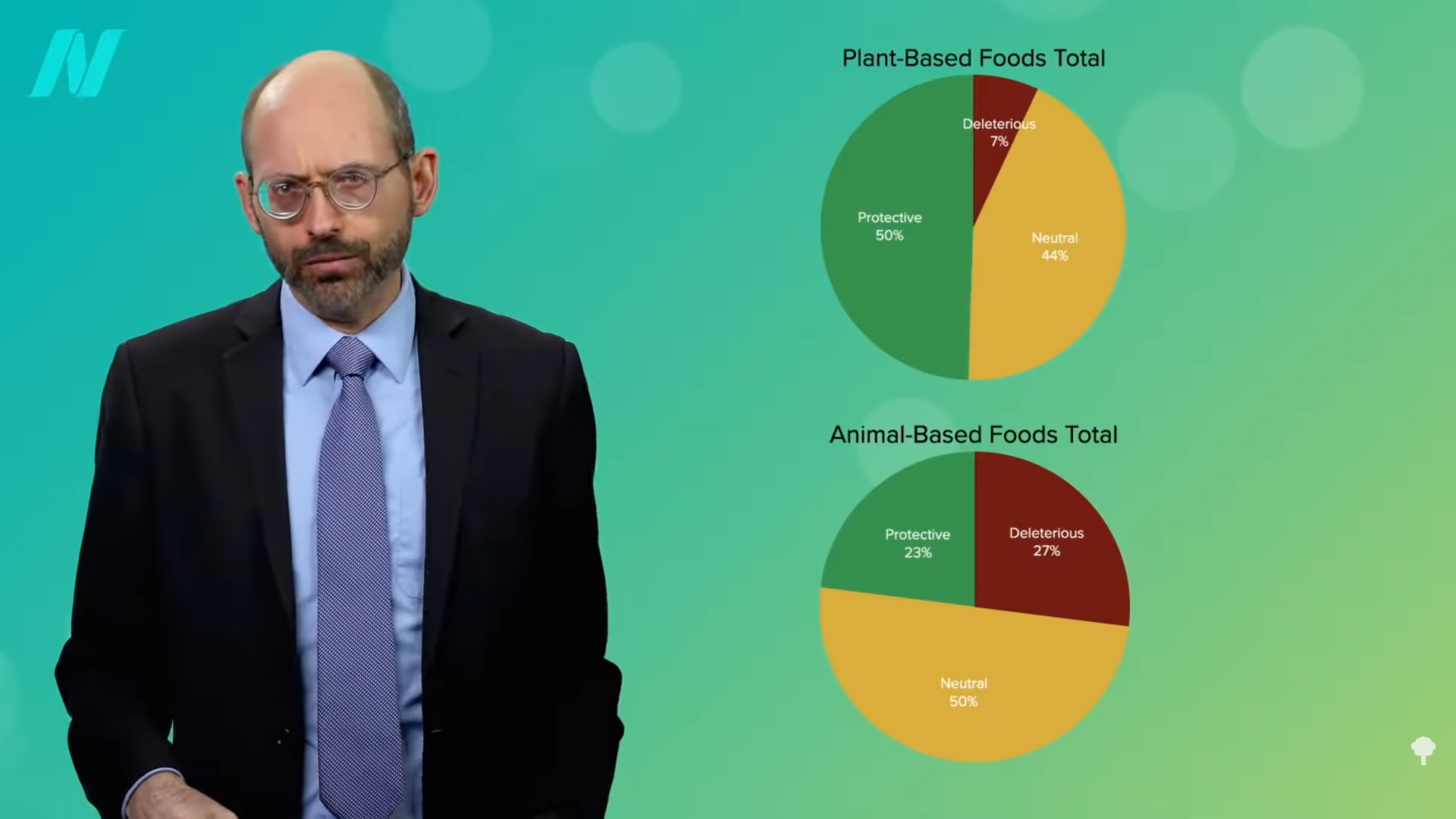
Let’s break these down. As you can see in the graph below and at 1:23, the plant foods consistently rate uniformly well, reflecting the total, but the animal foods vary considerably. If it weren’t for dairy and fish, the total for animal foods would swing almost entirely neutral or negative.
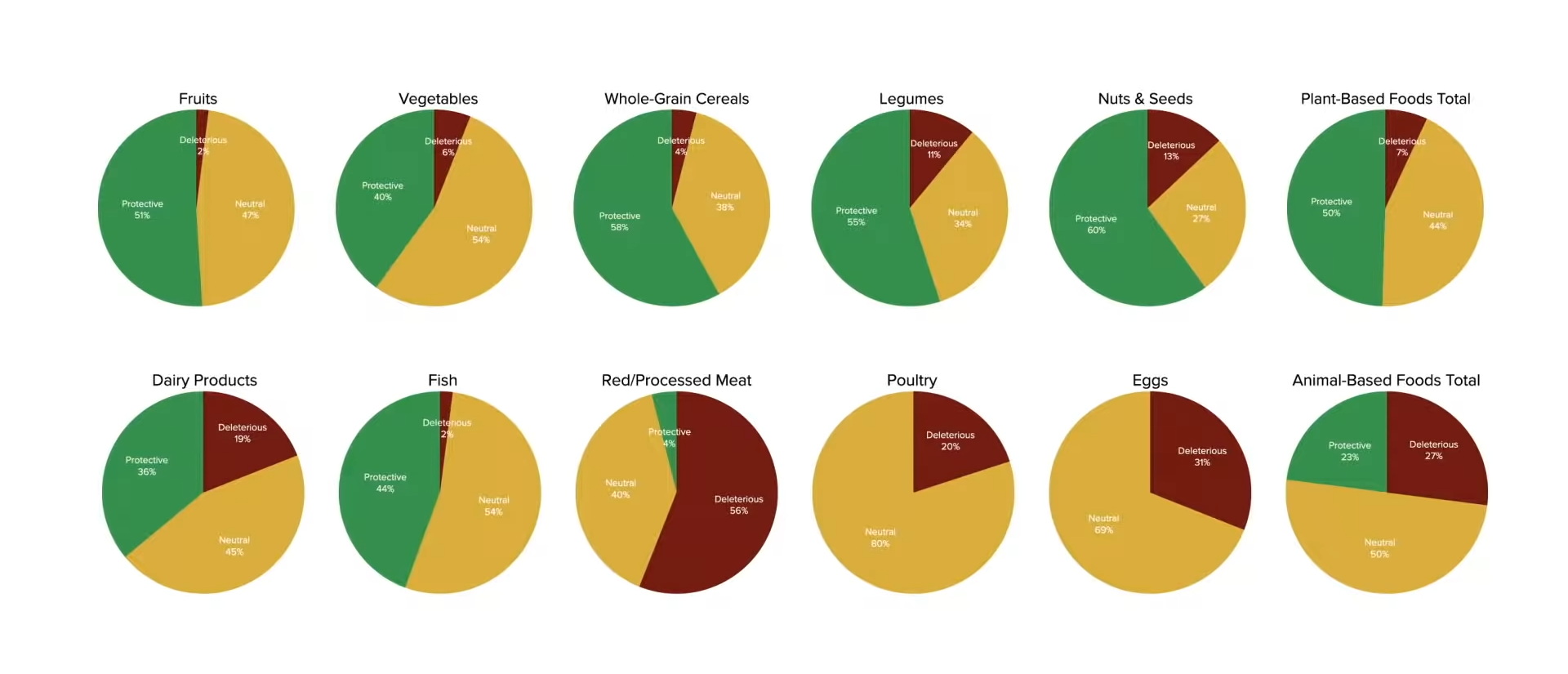 I talked about the effects of funding by the dairy industry in my last blog, as well as substitution effects. For instance, those who drink milk may be less likely to drink soda, a beverage even more universally condemned than dairy, so the protective effects may be relative. They may arise not necessarily from what is being consumed, but rather from what is being avoided. This may best explain the fish findings. After all, the prototypical choice is between chicken and fish, not chicken and chickpeas.
I talked about the effects of funding by the dairy industry in my last blog, as well as substitution effects. For instance, those who drink milk may be less likely to drink soda, a beverage even more universally condemned than dairy, so the protective effects may be relative. They may arise not necessarily from what is being consumed, but rather from what is being avoided. This may best explain the fish findings. After all, the prototypical choice is between chicken and fish, not chicken and chickpeas.
Not a single review found a single protective effect of poultry consumption. Even the soda industry could come up with 14 percent protective effects! But, despite all of the funding from the National Chicken Council and the American Egg Board, chicken, and eggs got big fat goose eggs, as you can see below and at 2:20 in my video.
Also, like the calcium in dairy, there are healthful components of fish, such as the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Not for heart health, though. In “the most extensive systematic assessment of effects of omega-3 fats on cardiovascular health to date,” increasing intake of fish oil fats had little or no effect on cardiovascular health. If anything, it was the plant-based omega-3s found in flaxseeds and walnuts that were protective. The long-chain omega-3s are important for brain health. Thankfully, just like there are best-of-both-worlds non-dairy sources of calcium, there are pollutant-free sources of the long-chain omega-3s, EPA, and DHA, as well.
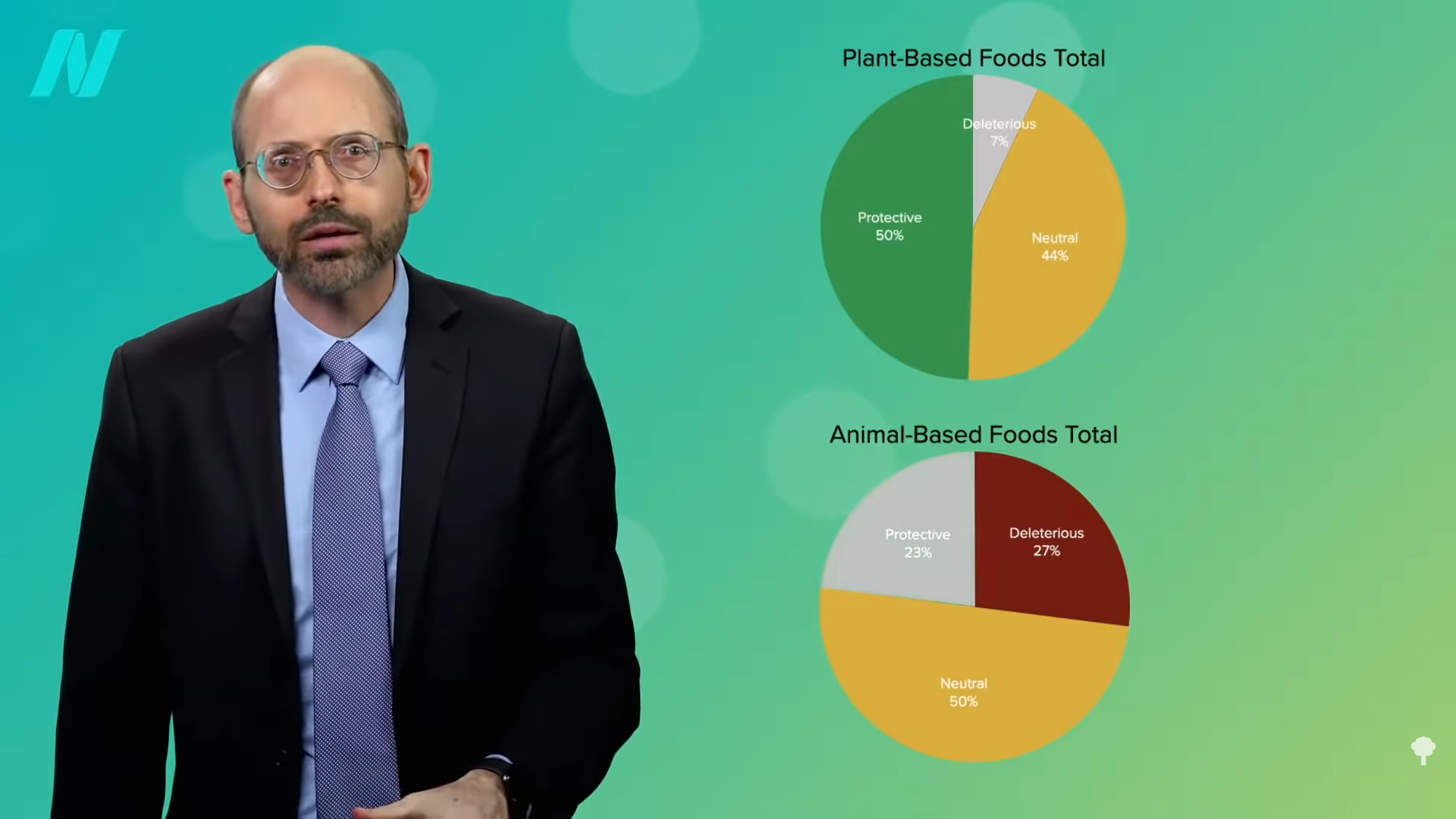
The bottom line, as you can see below and at 3:04 in my video, is that when it comes to diet-related diseases, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, mental health, bone health, cardiovascular disease, and cancers, even if you lump together all the animal foods, ignore any industry-funding effects, and just take the existing body of evidence at face value, nine out of ten study compilations show that whole plant foods are, in the very least, not bad.

However, about eight out of ten of the reviews on animal products show them to be not good, as shown in the graph below and at 3:24 in my video.
This reminds me of my Flashback Friday: What Are the Healthiest Foods? video, which you may find to be helpful for some broad takeaways.
If you missed my previous video, check out Friday Favorites: What Are the Best Beverages?.
The omega-3s video I mentioned is Should Vegans Take DHA to Preserve Brain Function?.
For more on eggs, see here.
On fish, go here.
And, for poultry, see related posts below.


Recent Comments